文件查找概述
为什么需要查找
很多时候我们可能会忘了文件所在的位置,此时就需要通过find来查找
有时候需要通过内容查找到对应的文件,此时就需要通过find来查找
find /etc -type f | xargs grep "blue.yn.cn"
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0:IPADDR=blue.yn.cn为什么是find
因为find命令可以根据不同的条件来进行查找文件
比如:
可以通过如上几种方式查找文件,从而实现精准定位
find命令语法
命令
路径
选项
表达式
动作
find
[path...]
[option]
[expression]
[action]
查找
地区
妹纸
18-25岁
???
find查找示例
find基于名称查找
# 创建文件
touch /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/{ifcfg-eth1,IFCFG-ETH1}
# 查找/etc目录下包含ifcfg-eht1名称的文件
find /etc/ -name "ifcfg-eth1"
# -i 忽略大小写
find /etc/ -iname "ifcfg-eth1"
# 查找/etc目录下包含ifcfg-eth名称所有文件
find /etc/ -name "ifcfg-eth*"
find /etc/ -iname "ifcfg-eth*"find基于大小查找
# 查找大于5M的文件
find /etc -size +5M
# 查找等于5M的文件
find /etc -size 5M
# 查找小于5M的文件
find /etc -size -5M
# 查找大于5M小于7M的文件
dd if=/dev/zero of=/root/big bs=6M count=1
find /etc -size +5M -a -size -7M | xargs ls -lh
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 6.0M 4月 12 11:21 /root/big基于类型查找
# f 文件
find /dev -type f
# d 目录
find /dev -type d
# l 链接
find /dev -type l
# b 块设备
find /dev -type b
# c 字符设备
find /dev -type c
# s 套接字
find /dev -type s
# p 管道文件
find /dev -type pfind基于时间查找
# 创建测试文件
for i in {01..10};do date -s 202404$i && touch file-$i;done
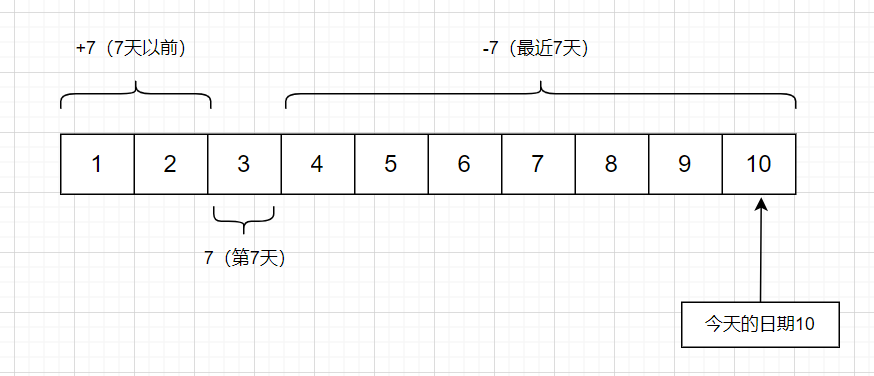
# 查找7天以前的文件
find ./ -iname "file-*" -mtime +7
# 查找第7天的文件
find ./ -iname "file-*" -mtime 7
# 查找最近7天的文件
find ./ -iname "file-*" -mtime -7
# 查找/var/log下所有以.log结尾的文件,并保留最近7天的log文件
find /var/log -type f -name "*.log" -mtime +7 -delete
# 查找最近120分钟内发生修改的文件
find ./ type f -mmin -120
# 查找系统有哪些命令在最近多长时间内,发生过变化
find /bin/ /sbin/ -type f -mmin -5find基于用户查找
# 查找属主是jack
find /home -user jack
# 查找属组是admin
find /home -group admin
# 查找属主是jack,属组是admin
find /home -user jack -group admin
# 查找属主是jack,并且属组是admin
find /home -user jack -a -group admin
# 查找属主是jack,或者属组是admin
find /home -user jack -o -group admin
# 查找没有属主
find /home -nouser
# 查找没有属组
find /home -nogroup
# 查找没有属主或属组
find /home -nouser -o -nogroupfind基于权限查找
-perm [/|-]MODE
MODE:精确权限匹配-MODE:每一类对象都必须同时拥有指定的权限(并且的关系)/MODE:任何一类(UGO)只要有一位匹配即可(或者的关系)
# 精确
find /root -type f -perm 644 -ls
# -包含(u涵盖6,并且g涵盖4,并且o涵盖4)
find /root -type f -perm -644 -ls
# /或者(u为6,或者g为4,或者o为0)
find /root -type f -perm /640 -ls
# 特俗权限
find /usr/bin/ /usr/sbin/ -type f -perm -4000 -ls
find /usr/bin/ /usr/sbin/ -type f -perm -2000 -ls
find /usr/bin/ /usr/sbin/ -type f -perm -1000 -lsfind逻辑运算符
符号
作用
-a
与(并且)
-o
或(或者)
-not/!
非(取反)
# 查找当前目录下,属主不是root的所有文件
find . -not -user root
find . ! -user root
# 查找当前目录下,属主属于hdfs,并且大小大于1k的文件
find . -type f -user hdfs -a -size +1k
# 查找当前目录下,属主为root或者以xml结尾的普通文件
find . -type f -a \( -user root -o -name '*.xml' \)find动作处理
查找到一个文件后,需要对文件进行如何处理,find的默认动作是-print
动作
含义
-print
打印查找到的内容(默认)
-ls
以长格式显示的方式打印查找到的内容
-delete
删除查找到的文件(仅能删除空目录)
-ok
后面跟自定义shell命令(会提示是否操作)
-exec
后面跟自定义shell命令 (标准写法 -exec \;
find结合exec
find /etc -name "ifcfg*" -exec cp -rvf{} /tmp \;
find /etc -name "ifcfg*" -exec rm -f{} \;find结合xargs
xargs将前者命令查找到的文件一个整体传递后者命令的输入,所以其处理性能极高exec是将文件一个一个的处理,所以处理性能极低
# 删除文件,性能对比
touch file-{1..10000}
find ./ -type -f -name "file-*" -exec rm -f {} \;
find ./ -type -f -name "file-*" | xargs rm -f
# 文件拷贝
find /usr/sbin/ -type f -perm -4000 | xargs -I {} cp -rv {} /tmpfind结合grep
当忘记重要配置文件存储路径时,可通过收索关键字获取文件其路径:
find /etc -type f | xargs grep "blue.yn.cn"
find /etc -type f | xargs grep -r "blue.yn.cn"
find /etc -type f | xargs grep -R "blue.yn.cn"
/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0:IPADDR=blue.yn.cn
留言